From Jan to Dec 2025, Non-China Global[1] Electric Vehicle Deliveries[2] Recorded About 7.662Mil Units, a 26.6% YoY Growth
- Volkswagen took top rank with 60.0% growth; Tesla remained 2nd on the list
From Jan to
Dec 2025, the total number of electric vehicles registered in countries around the world except China was
approx. 7.662 million units, a 26.6% YoY increase.
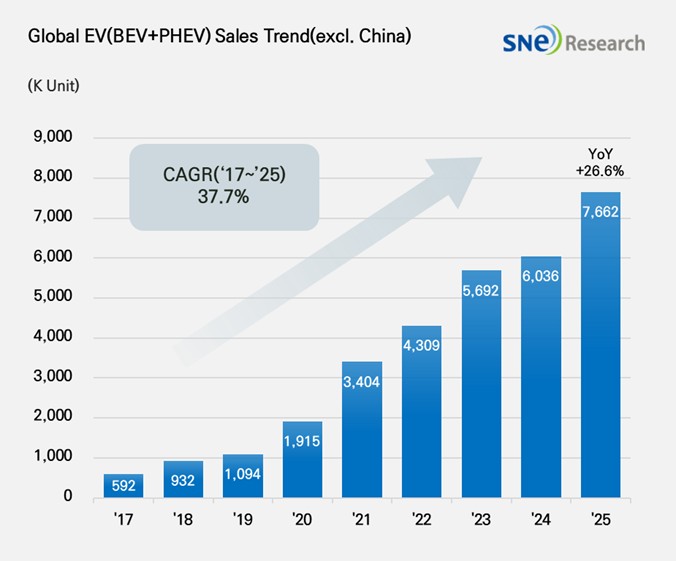
(Source: Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker – Jan 2026, SNE Research)
By corporate group, Volkswagen Group climbed to the top spot in the global electric vehicle (EV) market (excluding China), delivering 1.266 million units—a 60.0% increase year-on-year—and surpassing Tesla. This growth was driven primarily by the expanded sales of its flagship MEB platform-based models, such as the ID.4, ID.7, and ENYAQ, in the European market. The momentum further accelerated as sales of new models utilizing the PPE platform, including the Audi A6 e-tron, Q6 e-tron, and Porsche Macan 4 Electric, began in earnest. A key factor in strengthening their competitiveness within the non-Chinese market has been their strategy of linking a broad lineup—spanning from mass-market brands to premium and sports car segments—through a unified, shared platform strategy.
Tesla, which ranked second, delivered 1.01 million electric vehicles in the non-Chinese market—a 10.7% decrease year-on-year—resulting in its ranking dropping by one spot. The overall slowdown in demand was evident in its flagship models, with the Model Y and Model 3 declining by 6.7% and 11.5%, respectively. Furthermore, Model S (-53.9%) and Model X (-33.1%) both recorded double-digit drops due to intensifying competition and weakened price competitiveness within the luxury segment. Meanwhile, CyberTracker maintained its market presence with 24,000 units delivered, despite a 38.1% year-on-year decline within limited volume. However, its sales scale proved insufficient to offset the overall decline in Tesla's total performance.
Hyundai Motor Group secured the fourth spot, maintaining a relatively stable growth trajectory in the global market with approximately 609,000 electric vehicles sold, an 11.8% increase year-on-year. Within the battery electric vehicle (BEV) segment, the IONIQ 5 and EV3 led the group's performance, while compact and strategic models such as the Casper (Inster) EV, EV5, and Creta Electric are also receiving positive responses in key global markets. Conversely, existing flagship models like the EV6, EV9, and Kona Electric experienced a slowdown in sales, failing to sustain the same growth momentum seen in previous years. In the plug-in hybrid (PHEV) segment, a total of 104,000 units were delivered. SUV-focused models, including Sportage, Tucson, and Sorento, maintained a steady performance, whereas certain models like Niro and Ceed recorded a decline in sales.
By region, the group maintained its third-place position in the North American market in terms of sales volume, delivering approximately 166,000 units, following Tesla and GM. Despite a 19.6% year-on-year decline in North America, it is considered a significant achievement that the group sustained a performance surpassing major global competitors such as Ford, Stellantis, Toyota, and Volkswagen. Meanwhile, on January 26–27, Donald Trump mentioned the possibility of raising tariffs on South Korean electric vehicles from 15% to 25%. Should these remarks translate into actual policy, the price competitiveness of vehicles exported from South Korea to the United States could face a direct and substantial hit.
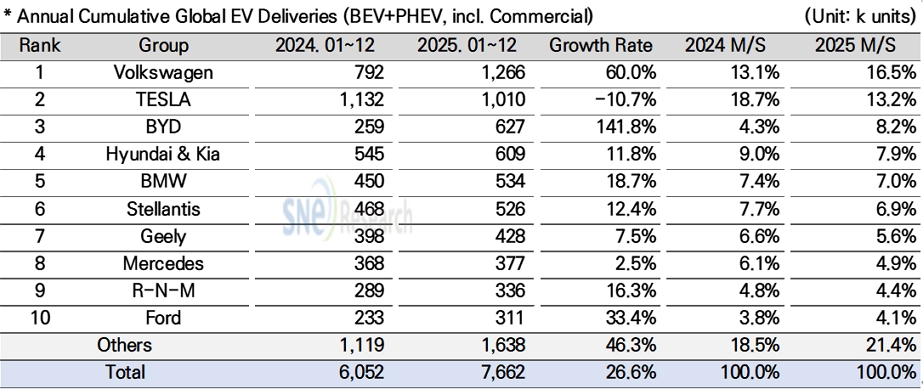
(Source: Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker – Jan 2026, SNE Research)
Europe saw a rebound with 4.257 million units delivered (a 34.9% increase), accounting for 55.6% of the global market. However, this recovery is not necessarily the result of subsidies or stricter regulations unilaterally driving up demand. Rather, it reflects a trend where demand has increased selectively for models with proven price competitiveness and robust product lineups, even amidst fluctuating regulatory signals. This is because policy uncertainty surrounding the EV transition is resurfacing, with recent movements to adjust the phase-out dates for internal combustion engines (ICE) or ease environmental regulations. These environmental shifts are directly impacting on the electrification strategies of legacy automakers. Major OEMs, including Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz, and BMW, appear to be adjusting the pace of their electrification rollouts or re-evaluating certain strategic roadmaps.
North America recorded 1.736 million units, a 5.0% decrease year-on-year. Following the expiration of the IRA-based Clean Vehicle Tax Credit after September 30, 2025, the policy leverage that effectively lowered the perceived purchase price for consumers weakened. This has increased the likelihood of further demand deceleration, particularly in mid-to-low-end segments where price sensitivity is high. Consequently, OEMs are tightening their risk management by adjusting the rollout speed of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and optimizing their powertrain mix with HEVs and EREVs (Extended Range Electric Vehicles).
In contrast, the Asia region (excluding China) recorded robust growth of 58.5%, reaching 1.233 million units. In India, the market is expanding around entry-level models amidst intensifying competition among local players. Meanwhile, Thailand and Indonesia are strengthening their roles not only as consumer markets but also as key production and export hubs. Other regions (Middle East, South America, Oceania, etc.) also sustained their early-stage expansion, reaching 436,000 units (a 50.6% increase).
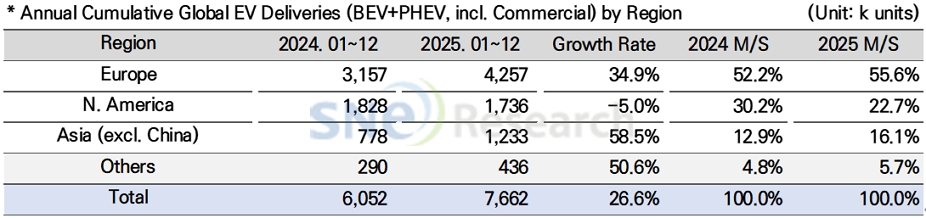
(Source: Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker – Jan 2026, SNE Research)
The most pressing recent issues are trade barriers and incentive uncertainties, which are significantly increasing market complexity. In the EU, the introduction of tariffs and regulatory flexibility is shifting the market focus from being policy-driven toward competition centered on price, product value, and localized production. In the United States, alongside changes in IRA requirements, Donald Trump’s recent remarks regarding a potential 25% tariff on electric vehicles have emerged as a critical new variable.
While this increases uncertainty for South Korean exports to the U.S., Hyundai Motor Group has the potential to partially buffer these tariff risks by expanding local production at the Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America (HMGMA) in Georgia. However, if the scope of these tariffs extends to components, even U.S.-assembled volumes may face cost pressures. Consequently, in the short term, the speed of supply chain localization, product mix, and pricing strategies will be the decisive factors.
In summary, while the market sustained growth in 2025, the primary drivers have shifted from policy-led expansion to profitability, supply chain resilience, and price competitiveness. A trend of moderate growth is expected to continue into 2026, yet regional volatility will likely intensify due to shifts in tariffs, regulations, and incentives. Future market dominance will be determined less by technology alone and more by cost structures, localization capabilities, and the speed of response to policy changes.
[2] Based on electric vehicles (BEV+PHEV) delivered to customers or registered during the relevant period

