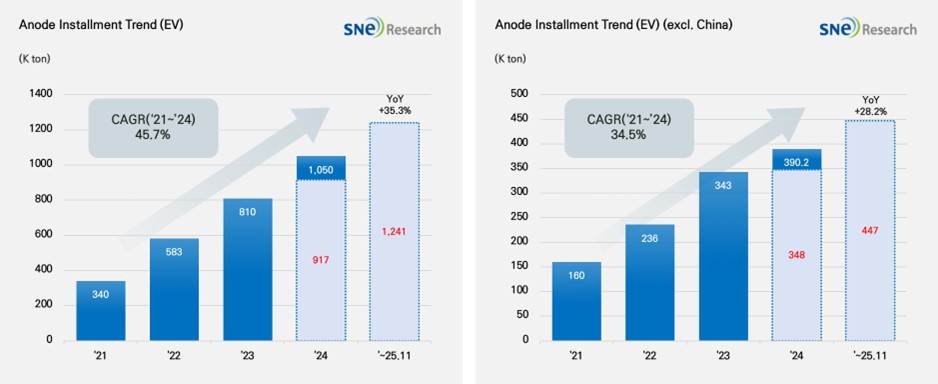
From Jan to Nov 2025, Global[1] Electric Vehicle Battery Anode Material Installment[2] Reached 1,241K ton, a 35.3% YoY Growth
- Anode installment in the non-China market recorded 447K ton, a 28.2% YoY growth
(Source: 2025 Dec Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
From Jan to Nov 2025, the total installment of anode materials in electric vehicles (EV, PHEV, HEV) registered worldwide was approx. 1,241K ton, posting a 35.3% YoY growth and staying in an upward trend. During the same period, in the global market outside China, the total installment of anode material was 447K ton, recording a 28.2% growth. Despite relatively moderate growth, the overall trend of steady growth was maintained.
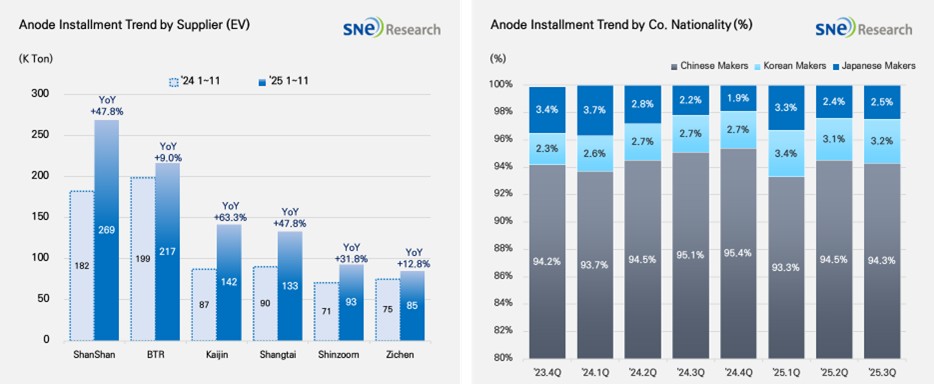
If we look at the market share held by companies, ShanShan (269K ton) and BTR (217K ton) ranked 1st and 2nd on the list, leading the global anode market. These two companies have successfully secured a broad customer base and mass production capabilities, by supplying anode materials to major battery makers such as CATL, BYD, and LG Energy Solution. Kaijin(142K ton), Shangtai(133K ton), Shinzoom(93K ton), and Zichen(85K ton) were all ranked high, exhibiting a double-digit YoY growth and expanding their presence in the global market.
(Source: 2025 Dec Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
If we look at the market shares of companies by their nationality, the Chinese anode makers accounted for more than 94% of the entire market share, solidifying their absolute dominance in the market. Based on expansion of production capacity and sophistication of technology, they have been solidifying their market dominance. With the electric vehicle market expanded, more Si-anode has been adopted, leading them to further intensify cooperation with major battery makers. Although the market shares taken by the Korean anode makers were only around 3.2%, cooperation with major cell makers has expanded to enter the market in earnest. Those efforts to cooperate with cell makers are mainly led by POSCO and Daejoo. On the other hand, the Japanese anode manufacturers accounted for only 2.5% of the market share, showing a relatively insignificant presence in the market. For instance, Hitachi and Mitsubishi maintained their conservative strategies to depend on the existing customer base, which seemed to gradually weaken their competitiveness in the market.
The anode material market has recently shifted from simple volume expansion to a stage where changes in EV demand structures are directly reflected in material selection. As both entry-level and mid-to-large EVs expand simultaneously, battery cell manufacturers are prioritizing a balance between lifespan, stability, and cost over mere energy density. In this process, the ability to ensure a stable supply of high-purity graphite-based anodes is re-emerging as a core competitive factor.
The adoption of silicon-composite anodes remains at a stage of supplementing existing graphite rather than achieving rapid replacement. While their application is increasing in some high-performance cells, graphite anodes—with proven durability and yield—are likely to maintain a high market share for the time being, especially amid the proliferation of LFP batteries and mass-market EVs.
In this environment, the market dominance of Chinese players is more likely to persist through the expansion of their customer bases and product portfolios rather than weakening in the short term. Conversely, for South Korean anode manufacturers, a strategy that combines customized products for specific cell/OEM platforms, silicon-composite technology, and non-Chinese sourcing options is emerging as a more realistic entry path than engaging in large-scale mass-production competition.
[2] Based on batteries installed to electric vehicles registered during the relevant period.

