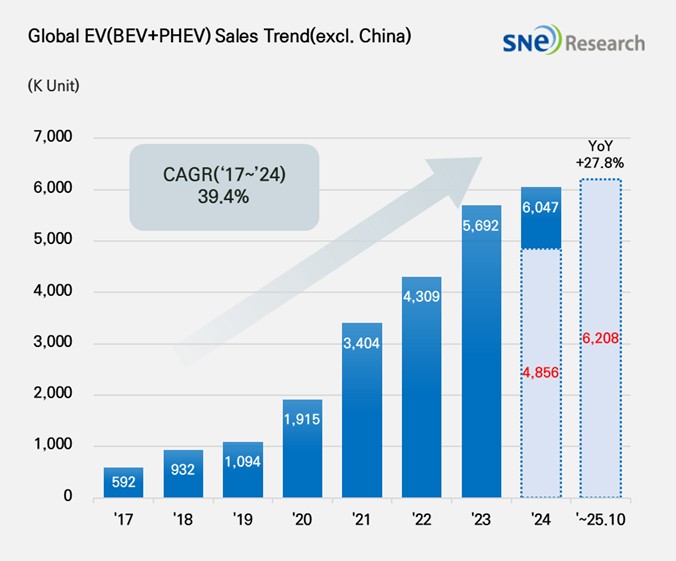
From Jan to Oct 2025, Non-China Global[1] Electric Vehicle Deliveries[2] Recorded About 6.208 Mil Units, a 27.8% YoY Growth
- Tesla ranked 2nd; VW ranked 1st by posting 64.4% growth
From Jan to Oct 2025, the total number of electric
vehicles registered in countries around the world except China was approx. 6.208
million units, a 27.8% YoY increase.
(Source: Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker – Nov 2025, SNE Research)
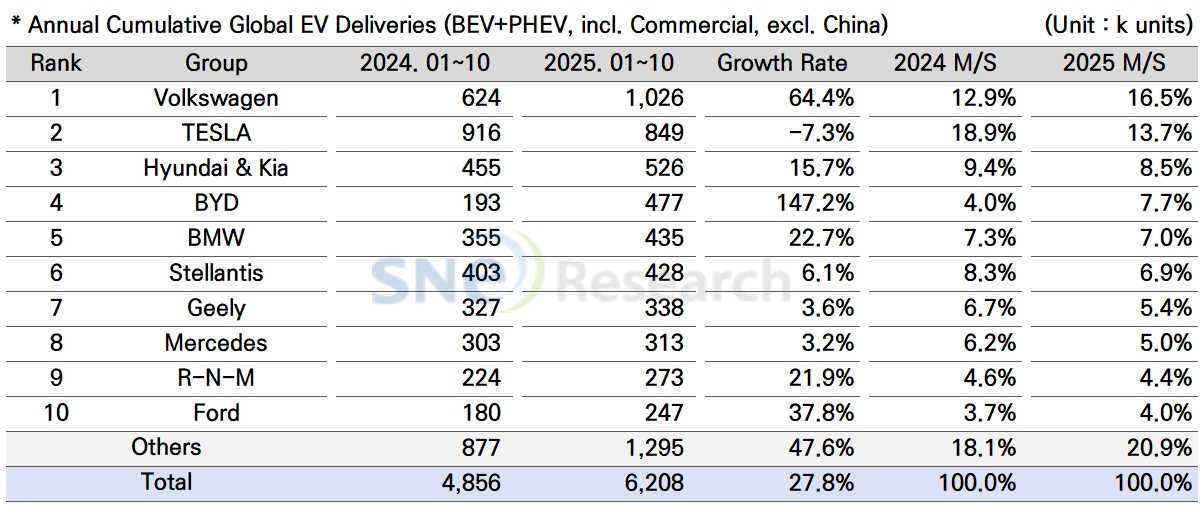
By group, Volkswagen Group remained top on the list by posting a 64.4% YoY increase with 1.026 million units sold. Major models such as ID.3, ID.7, ENYAQ, and ELROQ, built on the MEB platform, showed strong sales momentum in the European market. Increasing sales of new vehicles, such as A6/Q6 e-Tron and Macan 4 Electric, to which the PPE platform is applied, are regarded as a drive behind such rapid growth of VW Group.
Tesla took the 2nd position by delivering 849k units and posting a 7.3% YoY decrease. Deliveries of Model Y and 3 reduced by 2.8% and 8.2% respectively, showing that Tesla has been experiencing a slowdown in demand for its major models. Sales of premium sedans, Model S (-54.0%) and Model X (-35.1%) also showed a double-digit decrease. Cybertruck also recorded a 32.3% YoY decline in sales with only 21k units delivered to customers. Given the limited supply of Cybertruck, the number of deliveries during the relevant period can be regarded noticeable, but it was not sufficient to make a meaningful contribution to recovery of overall sales.
Hyundai Motor Group in the 3rd place sold approx. 526k units, posting a 15.7% YoY increase. In terms of BEV, IONIQ 5 and EV 3 were leading the growth of sales, while small-sized, strategic models such as Casper (Inster) EV, EV 5, and Creta Electric received positive feedback from the market. On the other hand, some of the existing models such as EV 6, EV 9, and Kona Electric showed a slowdown in sales, failing to maintain their growth momentum. Hyundai delivered a total of 90k units of PHEVs, with Sportage, Tucson, and Sorento maintaining a steady trend of sales, while Niro and Seed experienced a visible slowdown in sales.
Hyundai delivered 148k units in the North American market, ranking 3rd in the market and following Tesla and GM. Despite posting 13.0% YoY decline in the North American market, Hyundai still outperformed its major competitors such as Ford, Stellantis, Toyota, and Volkswagen. With the expanded sales of EV 3 in the global market, Hyundai has been diversifying its electrification portfolio by adding new line-ups such as EV 4 and IONIQ 9. By expanding the proportion of local production and infrastructure, Hyundai is expected to sustain a stable profit structure amidst market volatility caused by changing tariff and subsidy policies.
(Source: Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker – Nov 2025, SNE Research)
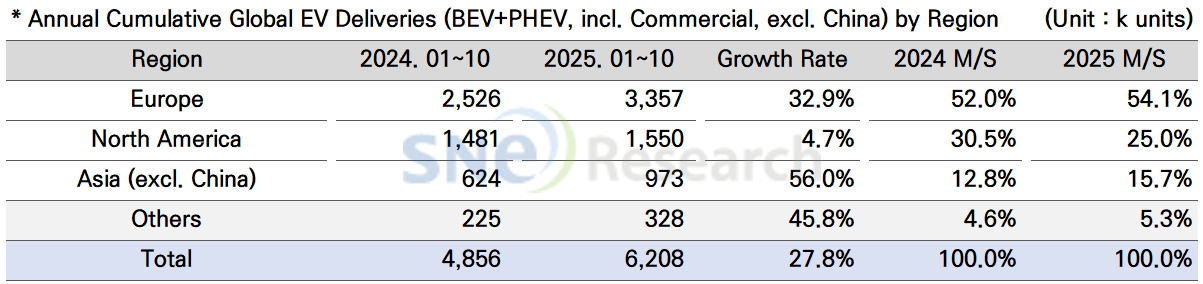
In Europe, a total of 3.357 million units of electric vehicles were sold, posting a 32.9% YoY growth and taking up 54.1% of global market share except China. Recently, the growth of European EV market was led by mid-size SUVs and crossover vehicles such as ID.4, Q4 e-Tron, EV3, Elroq, and iX1. These models, designed for practical family-oriented demand, combine high efficiency and affordable pricing while leveraging universal electrification platforms such as MEB and PPE, driving rapid market expansion. Moreover, major OEMs including Volkswagen, Volvo, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz are strengthening platform integration strategies to improve production efficiency and simplify their model lineups. This trend is emerging as a key factor reshaping the European EV market structure, shifting its focus toward mid-sized vehicles.
In the North American market, a total of 1.550 million units of electric vehicles were sold, recording a 4.7% YoY growth. The market share of North American market has slightly dropped to 25.0%. At the end of September, the expiration of consumer tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) led major OEMs to launch aggressive promotions aimed at clearing inventory and boosting sales, resulting in a short-term surge in EV deliveries. However, after that, the EV sales in October showed a 50% decrease from the previous month and 30% drop from the same month last year. On the other hand, GM, Ford, and Hyundai Motor Group are adjusting their strategies by reshaping their lineups around mid- to low-priced segments and expanding hybrid models. In the North American market, temporary volatility is increasing due to changes in tax policy, while local production share and price competitiveness are emerging as the key factors determining future market share.
The Asia market (excluding China) exhibited a 56.0% YoY growth with 973k units of electric vehicles sold, accounting for 15.7% of global market share excluding China. In India, the adoption of small electric vehicles priced between USD 10,000 and 20,000 is expanding rapidly, with Tata Motors and Mahindra leading market growth. In Thailand and Indonesia, Chinese OEMs such as BYD, SAIC, and Chery have begun full-scale operation of local plants, strengthening these countries’ positions as regional production hubs. In contrast, global OEMs are responding by focusing on localized pricing strategies and model customization tailored to local demand structures, prioritizing market adaptability over the speed of electrification. In Japan, Toyota and Honda continue to pursue hybrid-centered strategies while gradually expanding their BEV lineups.
In other regions—including the Middle East, Latin America, and Oceania—EV sales reached 328k units, a 45.8% increase year-on-year, accounting for 5.3% of global market share. These regions remain in the early stages of EV market development, with significant disparities in government policy support and infrastructure readiness across countries. While government-led adoption programs and aggressive market entry by Chinese OEMs are driving some progress, limited charging infrastructure and high vehicle prices continue to be the main constraints on broader EV adoption.
(Source: Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker – Nov 2025, SNE Research)
In 2025, the global electric vehicle (EV) market—excluding China—is showing increasingly clear divergence across major regions, driven by differences in policy changes and demand structures. In November, the European Union and China agreed to cancel high tariffs on Chinese EVs and instead introduce a minimum price system. Separately, the German government is requesting that hybrids be exempted from the EU’s planned 2035 ban on new internal combustion engine vehicles.
In the United States, the passenger EV tax credit expired on September 30, shifting policy focus away from incentives for household battery EVs toward commercial and fleet vehicles. Against this backdrop, global automakers are responding to differing regional regulations and transition speeds through cost-efficiency strategies, including technology in-house development, local sourcing, and the expansion of low-cost, hybrid, and LFP-based models.
[2] Based on electric vehicles (BEV+PHEV) delivered to customers or registered during the relevant period

