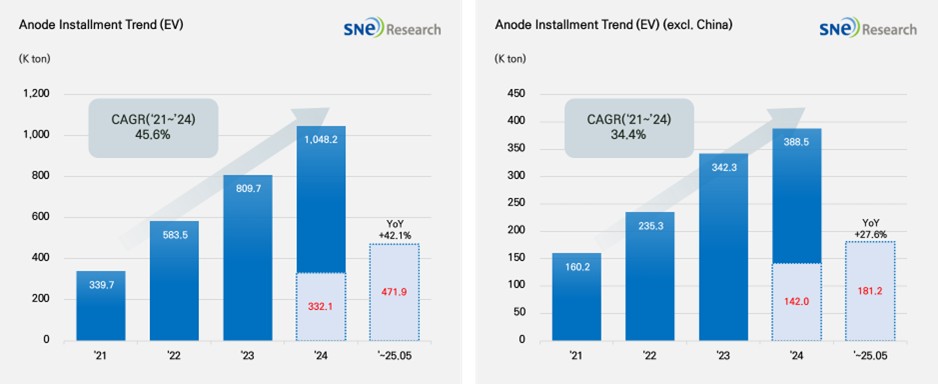
From Jan to May in 2025, Global[1] Electric Vehicle Battery Anode Material Installment[2] Reached 471.9K ton, a 42.1% YoY Growth
- The non-China
market recorded 181.2K ton, posting a 27.6% growth
(Source: 2025 June Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
From Jan to May in 2025, the total installment of anode materials used in electric vehicles (EV, PHEV, HEV) registered worldwide was approx. 471.9K ton, posting a 42.1% YoY increase and maintaining steady growth. In the non-China market, the total installment of anode materials was 181.2K ton, recording a 27.6% growth. Despite the growth was relatively moderate, the overall trend of steady growth was maintained.
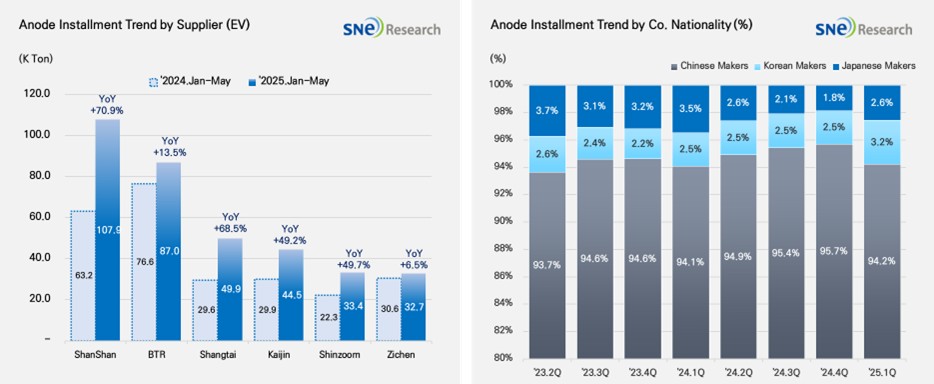
If we look at the market shares of companies, ShanShan (107.9K ton) and BTR (87.0K ton) ranked 1st and 2nd on the list, leading the global anode market. The two companies secure a stable customer basis and mass production capabilities, supplying to major battery makers such as CATL, BYD, and LGES. Shangtai(49.9K ton), Kaijin(44.5K ton), Shinzoom(33.4K ton), and Zichen(32.7K ton) were also in the high rank, exhibiting a high growth of 40~70% compared to the previous year.
(Source: 2025 June Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
If we look at the market shares of companies by their nationality, the Chinese anode makers accounted for about 95% of the entire market share, keeping their absolute dominance in the market. Based on expansion of production capacity and sophistication of technology, they have been solidifying their market dominance. With the electric vehicle market expanded, more Si-Anode has been adopted, leading them to further consolidate cooperation with major battery manufacturers. The market shares held by the Korean anode makers hovered around 2.7%, but cooperation with major cell makers has been expanded mainly by POSCO and Daejoo, meaning that the Korean anode suppliers are trying in earnest to enter the market. On the other hand, the Japanese anode manufacturers accounted for only 2.0% of the market share, showing a relatively unnoticeable presence in the market. Hitachi and Mitsubishi maintained their conservative business management system relying on the existing customers, which seemed to gradually weaken their competitiveness in the market.
Recently, the global anode market continuously saw huge demand for graphite-based products, while the commercialization of Si-Anode has become noticeable, leading to technology conversion in the industry. Major Chinese anode companies have already established the mass production system for Si-Anode and been trying to increase the supply of Si-Anode in cooperation with large battery manufacturers such as CATL and BYD. In this regard, narrowing technology gaps and developing high-value-added products have been rising one of major competitiveness factors.
Meanwhile, the US and Europe are about to implement the strategies to lower their dependence on graphite from China by securing local refining facilities in North America and strengthening the IRA tax regulations to pursue independence from the Chinese materials. This current trend is leading the reorganization of global supply chain. Anode suppliers are, thus, required to come up with multi-faceted response measures such as expansion of local production bases in North America and Europe as well as sourcing raw materials from non-China regions.
In future, the anode market is highly likely to see stable demand for the existing graphite anode material and widespread usage of silicon-based, next-generation anode product, which is expected to create a dualistic competitive landscape. Anode manufacturers who have technological capabilities and stable supply chain are expected to lead the market in mid to long term, and the anode market is also forecasted to vary depending on different policies in each country.
[2] Based on batteries installed to electric vehicles registered during the relevant period.

