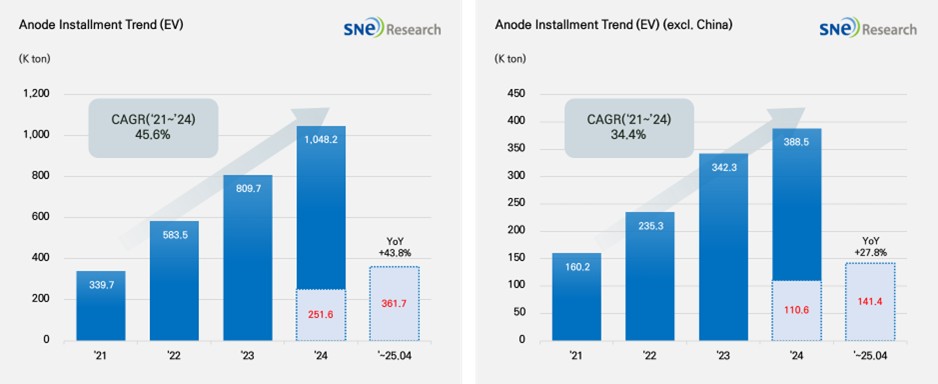
From Jan to Apr in 2025, Global[1] Electric Vehicle Battery Anode Material Installment[2] Reached 361.7K ton, a 43.8% YoY Growth
- The non-China market recorded 141.4K ton, posting a 27.8% growth.
(Source: 2025 May Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
From Jan to Apr in 2025, the total installment of anode materials used in electric vehicles (EV, PHEV, HEV) registered worldwide was approximately 361.7K ton, posting a 43.8% YoY growth and maintaining steady growth. In the non-China market, the total installment of anode materials was 141.4K ton, recording a 27.8% growth, but still keeping a relatively stable growth. Anode material is one of the key materials determining the performance of lithium-ion battery. Anode materials are becoming increasingly important, as they directly affect key factors in electric vehicle performance such as battery lifespan, charging speed, and energy density.
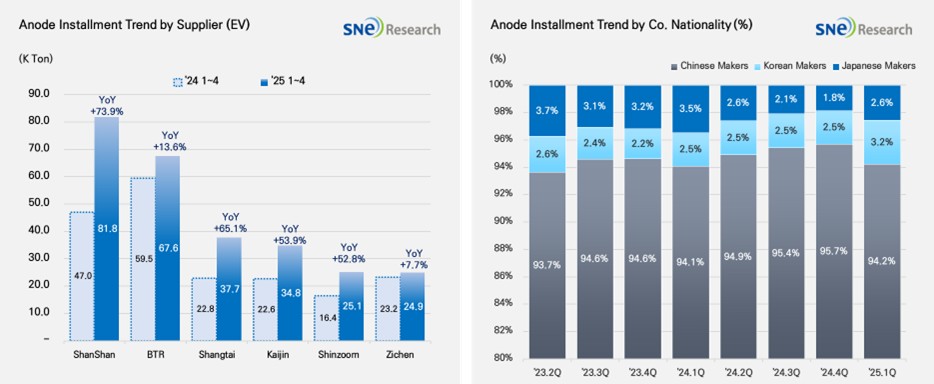
If we look at the market shares of companies, ShanShan and BTR ranked 1st and 2nd on the list, leading the global anode market. The two companies secure a broad range of customers by supplying to major battery makers such as CATL, BYD, and LGES. Shangtai, Kaijin, and Zichen also recorded over 25.0K ton of installment respectively, posting over 50% YoY growth.
(Source: 2025 May Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
If we look at the market shares of companies by their nationality, the Chinese anode companies boast an overwhelming dominance in the market, taking up approx. 94.2% of the entire market. They have been strengthening their market dominance by aggressively expanding their production capacities and sophisticating technologies. Specifically, in line with the increase of the electric vehicle market, more Si-Anode has been adopted, leading to further consolidation of cooperation between anode makers and major battery companies. On the other hand, although the Korean anode makers, such as POSCO and Daejoo, have been actively working to enter the market by expanding their cooperation with major cell makers, their market shares are still around 3.2%. The Japanese anode companies account for only 2.6% of the market share, showing an unnoticeable presence in the market. Hitachi and Mitsubishi maintained their conservative business management system focusing on the existing customers, which seemed to weaken their competitiveness compared to others.
Amid recent sharp fluctuations in raw material prices and escalating tariff tensions between the U.S. and China, supply chain risks in the global anode materials market are drawing increased attention. In particular, the U.S. has imposed high tariffs on key materials such as Chinese graphite and, through the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), restricted tax credits for electric vehicles containing Chinese-made components and minerals. As a result, there is growing pressure to structurally reorganize the anode supply chain, which is heavily depends on the Chinese suppliers. In response, the industry is increasingly prioritizing raw material diversification and geographically distributed production as key challenges, while also pursuing technological alternatives such as silicon-based anode materials and bio-based sources. Amid these shifts, companies in South Korea and Japan are also being called to establish responsive strategies. Korean firms are exploring opportunities to strengthen their market presence by expanding production bases in North America and focusing on high energy density and premium product lines. Meanwhile, Japanese companies – facing relatively limited global market share – need to expand their technology portfolios, pursue global strategic partnerships, and make bold investments in production capacity.
[2] Based on batteries installed to electric vehicles registered during the relevant period.

